In the ever-expanding realm of artificial intelligence, machines are not just crunching numbers or parsing text—they’re learning to read our emotions. Emotion recognition technology, once confined to science fiction, is now a fast-developing branch of AI with real-world applications that are already reshaping how we interact with technology, brands, and even each other.
What Is Emotion Recognition AI?
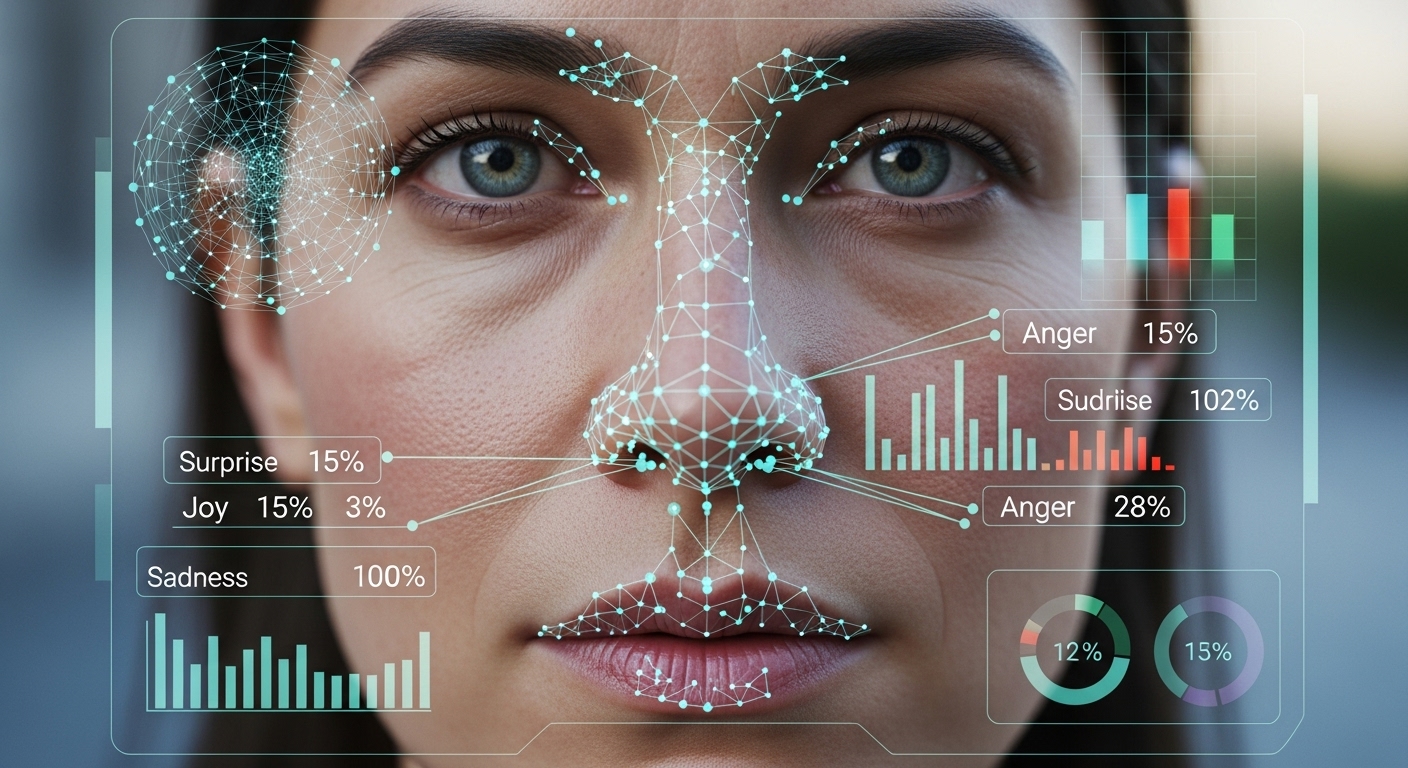
At its core, emotion recognition AI involves teaching machines to analyze facial expressions, voice tones, body language, and sometimes even biometric signals to identify human emotions. It relies heavily on computer vision and deep learning algorithms trained on massive datasets of human faces and expressions. By mapping muscle movements and micro-expressions, AI systems can determine whether a person is happy, sad, angry, surprised, or displaying more nuanced feelings like confusion or contempt.
How It Works
Using cameras and sensors, emotion recognition AI captures real-time data. This data is then processed through neural networks that have been trained to associate specific facial cues with emotional states. These systems go beyond surface-level observation; some even incorporate contextual awareness—factoring in a person’s age, culture, or situational context to better interpret expressions.
Where It’s Being Used
Emotion recognition technology is already showing up in surprising places:
- Retail: Brands are testing AI systems to gauge customer satisfaction by analyzing facial reactions to in-store displays or advertisements.
- Education: In virtual classrooms, AI can monitor students’ attention and engagement, helping teachers adapt their lessons in real time.
- Healthcare: Emotional AI is being used to detect early signs of mental health conditions like depression or anxiety, often through subtle facial and vocal cues.
- Automotive: Some cars are equipped with systems that monitor driver emotions to detect drowsiness or road rage, enhancing safety.
Ethical and Privacy Concerns
As promising as emotion recognition AI is, it also raises serious ethical questions. Critics warn about the potential for misuse in surveillance or discriminatory profiling. There’s also concern over consent—are people always aware their emotions are being tracked? Accuracy is another issue. Human emotions are complex, and cultural variations in expression mean that AI can misinterpret signals, especially in diverse or high-stress environments.
The Future of Emotional Intelligence in Machines
Emotion recognition is pushing AI toward a new frontier: emotional intelligence. As machines become better at sensing human emotions, they will also need to learn how to respond appropriately—whether it’s a digital assistant calming a frustrated user or a customer service bot offering empathy during a complaint.
The ultimate goal isn’t to replace human empathy, but to augment it. In the future, emotionally aware machines could become better companions, more intuitive tools, and safer collaborators in everything from healthcare to education.
As this technology continues to evolve, the key will be balancing innovation with responsibility—ensuring that emotional intelligence in AI serves people, respects privacy, and remains firmly under ethical control.